radiomics方法整理各论文方法整理。
Y. Zhu et al 2019 A deep learning radiomics model
Y. Zhu et al., “A deep learning radiomics model for preoperative grading in meningioma,” European Journal of Radiology, vol. 116, pp. 128–134, Jul. 2019.
2 个医院的数据(99 in the primary cohort and 82 in the validation cohort)
对于手工特征:
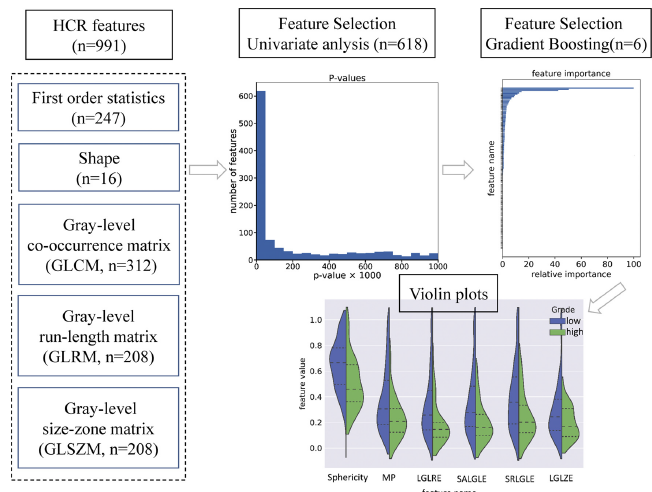
为了解决样本不均衡问题,作者采用了过采样技术 SMOTE.
单变量分析(Mann-Whitney U tests),选择了 $p < 0.05$ 的特征。
- 梯度提升方法选择特征。
- 构造了 SVM 分类器。
对于深度特征:
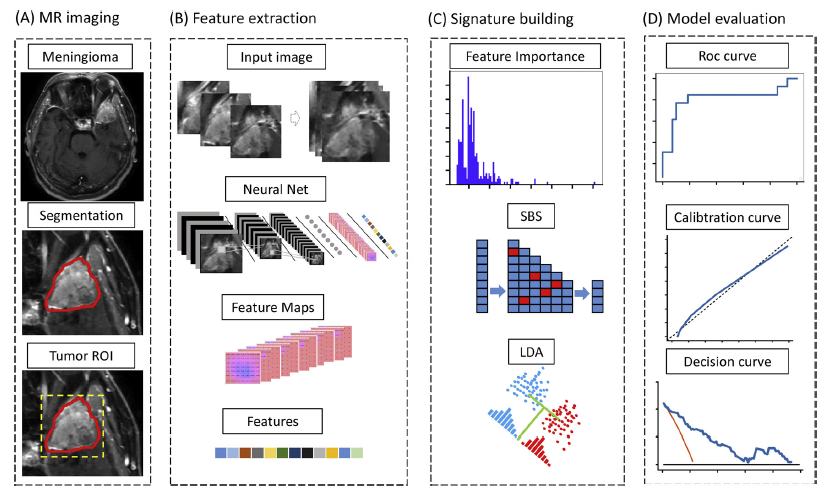
- 先用随机森林进行特征选择,重要性大于 0.001 的保留。
- 再用 sequential backward selection (SBS)。
- 线性判别分析进行分类。
- 由于样本不均衡,在特征选择和建模时,采取了 bagging 的技术。
融合特征:
- SVM 分类。
F. Liu et al., 2018 Development and validation of a radiomics signature
F. Liu et al., “Development and validation of a radiomics signature for clinically significant portal hypertension in cirrhosis (CHESS1701): a prospective multicenter study,” EBioMedicine, vol. 36, pp. 151–158, Oct. 2018.
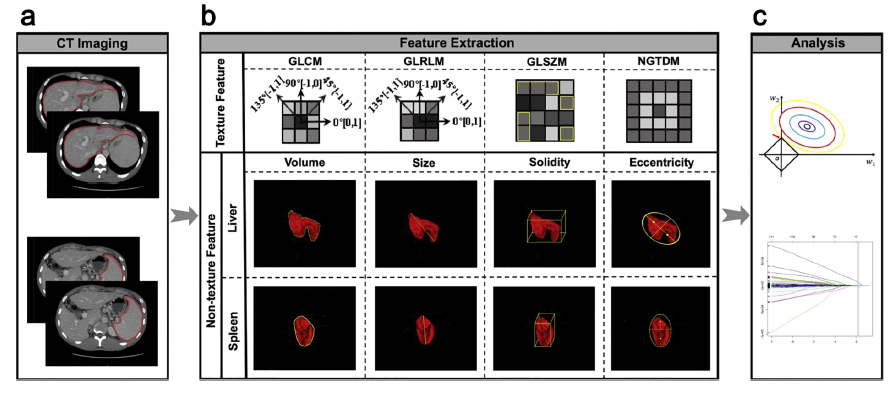
样本数量:385 patients with cirrhosis from five liver centers in China.
特征选择:LASSO
S. Wang *et al 2019 Deep learning provides a new computed
S. Wang et al., “Deep learning provides a new computed tomography-based prognostic biomarker for recurrence prediction in high-grade serous ovarian cancer,” Radiotherapy and Oncology, vol. 132, pp. 171–177, Mar. 2019.
样本数量:245 patients with HGSOC from two hospitals, which included a feature-learning cohort (n = 102), a primary cohort (n = 49) and two independent validation cohorts from two hospitals (n = 49 and n = 45).
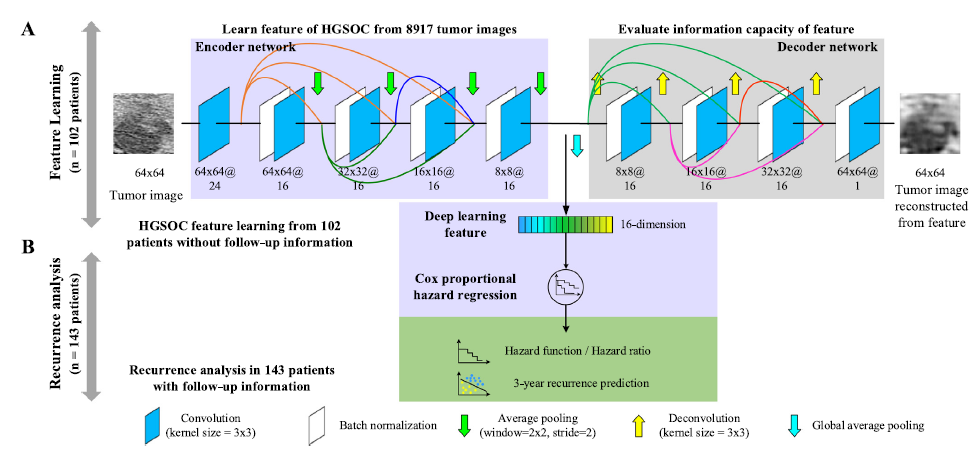
做了一个 auto-encoder,提取中间层的数据作为特征进行分析。
Cancer Letters - Qian_2019_Differentiation of glioblastoma
Z. Qian et al., “Differentiation of glioblastoma from solitary brain metastases using radiomic machine-learning classifiers,” Cancer Letters, vol. 451, pp. 128–135, Jun. 2019.
研究目的:术前区分确定术前将胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)与孤立性脑转移瘤(MET)。
样本数量:412个样本(242个GBM,170个MET)分成训练集(227)和测试集(185)。
特征提取:
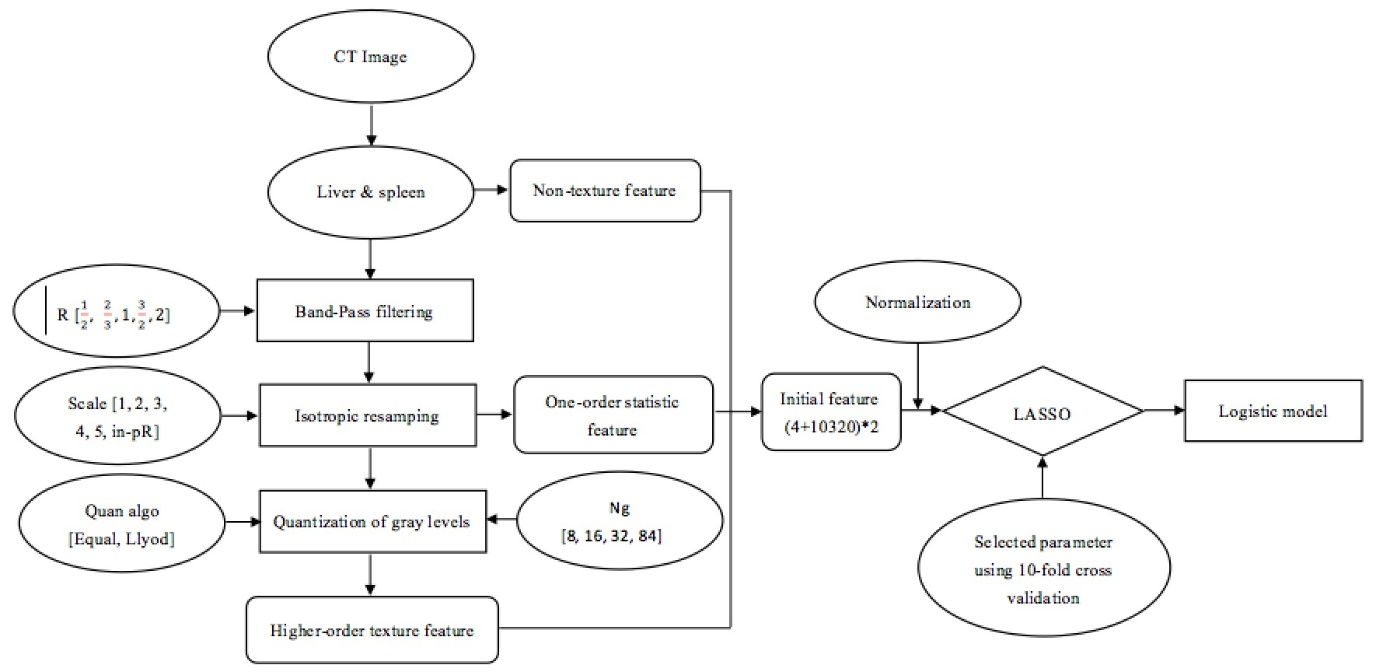
- 使用了PyRadiomics库。将所有的图像归一化到0-100像素内,并重采样到3mm的分辨率。提取了1303个特征。2个医生画的roi区域,分别提取特征,ICCs大于0.8的保留(898个),然后选择其中年长的医生提取的特征进行分析。构建了一个无监督k均值聚类,大概看看GBM和MET可不可分。
模型构造:
12种特征选择方法。(使用了R和python)
EUDT_38, FAOV_41, GNRO_17, IFGN_31, LASSO_24,LG_4, MUIF_35, RELF_17, RF_43, SVM_3, TSCR_50, and WLCX_46.
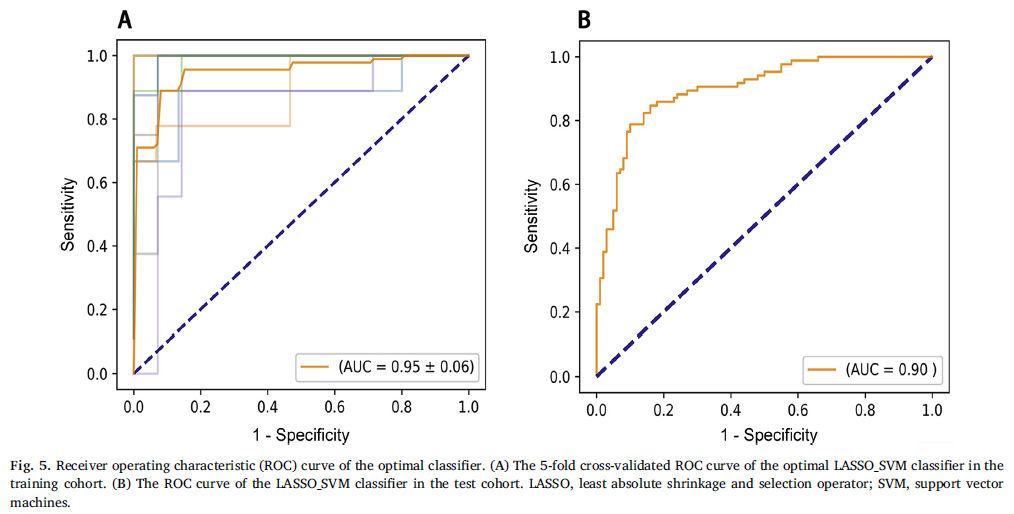
7个分类器。(sklearn)在训练集中做5折交叉验证,在训练集中AUC≥0.95 和 RSD≤6 的分类器,和在测试集中 AUC 最高的 model 最为最终考虑的 model.
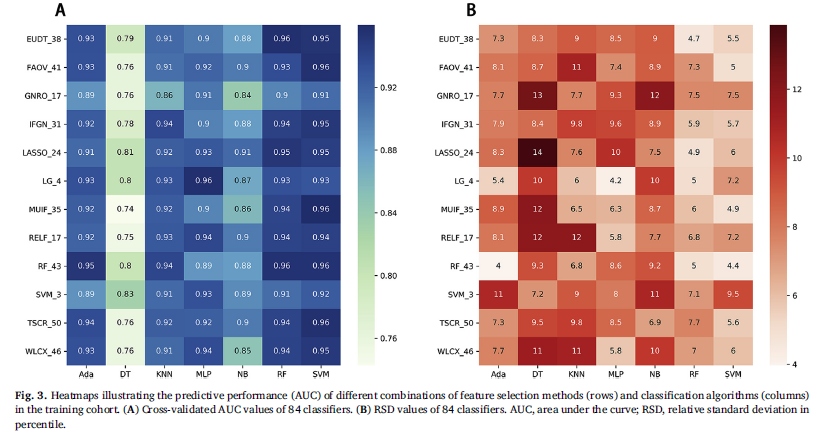
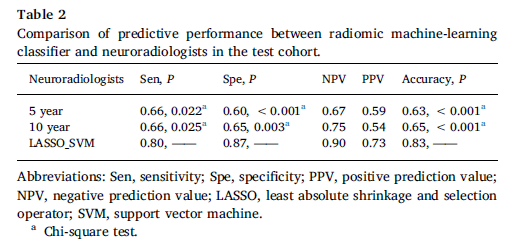
- 根据交叉验证的结果,选择了 13 个 model,然后应用于 test 数据集。LASSO_SVM效果最好。还与医生的诊断结果进行了对比。

npj Precis. Onc. - Nasief_2019_A machine learning based delta-radiomics
H. Nasief et al., “A machine learning based delta-radiomics process for early prediction of treatment response of pancreatic cancer,” npj Precis. Onc., vol. 3, no. 1, p. 25, Dec. 2019.
纵向图像中的 radiomic 特征随时间的变化(delta radiomics)可以潜在地用作预测治疗反应的生物标记。
样本数量:回顾性分析90例胰腺癌患者在常规 CT 引导化学放疗期间获得的常规CT,证明了这一过程。共分析了2520 个 CT(28-daily-fractions-per-patient)),并对其病理反应进行了分析。50名患者进行训练,并使用留一法交叉验证,其余40位患者的数据进行了外部独立验证。
delta-radiomics 特征选择
基于 Spearman 相关系数,选择了 73 个特征。
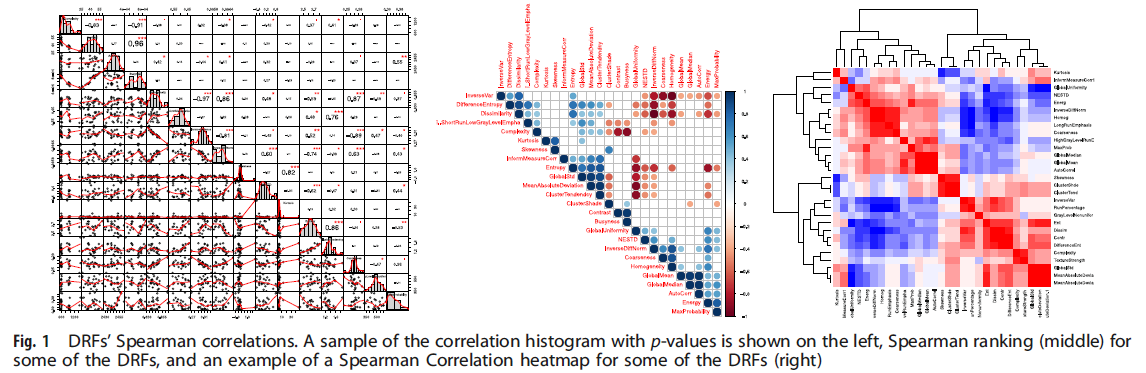
线性回归分析发现,有27个特征表现出与病理反应相关的趋势。
基于 t 检验和线性混合效应模型的分析,发现 27 个选定的DRF中有 13 个通过了两项检验,p < 0.05 ,表明它们与病理反应之间存在显着相关性。
Nat Commun, - Elshafeey_2019_Multicenter study demonstrates radiomic features
N. Elshafeey et al., “Multicenter study demonstrates radiomic features derived from magnetic resonance perfusion images identify pseudoprogression in glioblastoma,” Nat Commun, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 3170, Dec. 2019.
样本数量:98

- We first ranked features based on their relevance to the outcome and within-feature redundancy using the MRMR feature selection technique. 首先使用MRMR方法进行特征选择。
- Subsequently, SVM with linear kernel and C5.0 models were constructed using the features selected by the MRMR analysis. Finally, the diagnostic performance of the models was evaluated using LOOCV for the SVM model and 10-fold cross-validation for the C5.0 model. SVM分类器和决策树C5.0分类器。
- 对于SVM模型,使用LOOCV评估模型;对于C5.0模型,使用10折交叉验证评估模型。
Nat Commun - Lu_2019_A mathematical-descriptor of tumor-mesoscopic-structure from computed-tomography
H. Lu et al., “A mathematical-descriptor of tumor-mesoscopic-structure from computed-tomography images annotates prognostic- and molecular-phenotypes of epithelial ovarian cancer,” Nat Commun, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 764, Dec. 2019.
样本数量:364例上皮性卵巢癌(EOC)患者。伦敦帝国学院294例以及TCGA的70例。
npj Breast Cancer - Huang _2019_Exploration of PET and MRI radiomic features for decoding breast cancer
S. Huang et al., “Exploration of PET and MRI radiomic features for decoding breast cancer phenotypes and prognosis,” npj Breast Cancer, vol. 4, no. 1, p. 24, Dec. 2018.
持续更新……

